Your Fukushima daiichi nuclear disaster summary images are ready in this website. Fukushima daiichi nuclear disaster summary are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens today. You can Get the Fukushima daiichi nuclear disaster summary files here. Find and Download all free photos.
If you’re looking for fukushima daiichi nuclear disaster summary images information connected with to the fukushima daiichi nuclear disaster summary interest, you have pay a visit to the ideal site. Our site always gives you hints for seeking the highest quality video and image content, please kindly hunt and find more enlightening video articles and graphics that match your interests.
Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Disaster Summary. The Prime Minister declared a nuclear emergency on the evening of. There were no coordinated arrangements at the national and local levels for responding to a nuclear emergency and a natural disaster occurring simultaneously. Major damage to the backup power and containment systems caused by the 2011 Tōhoku earthquake and tsunami resulted in overheating and leaking from some of the Fukushima I nuclear plants reactors. How many manatees are killed each year by boats what happened to the dr phil family 2020.
 Japan Astonishingly Unprepared For Fukushima Disaster Cnet From cnet.com
Japan Astonishingly Unprepared For Fukushima Disaster Cnet From cnet.com
The next day 12th in the early morning the leakage of radioactive materials had been found in front of the main gate of the nuclear. The IAEA confirms extremely high levels of radioactive caesium were deposited northwest of the reactor site. The 90-magnitude quake was so forceful it shifted the Earth off its axis. Summary of the Fukushima Daiichi Disaster The earthquake on March 11 2011 off the east coast of Honshu Japans largest island reportedly caused an automatic shutdown of 11 of Japans 55 operating nuclear power plants. It triggered a tsunami which swept over the main island of Honshu killing more than 18000 people and wiping entire towns. Major damage to the backup power and containment systems caused by the 2011 Tōhoku earthquake and tsunami resulted in overheating and leaking from some of the Fukushima I nuclear plants reactors.
The tsunami resulting from the earthquake shut down the diesel generators and the main cooling system causing a series of nuclear meltdowns and hydrogen-air chemical reactions.
The accident at the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear plant was initiated by the March 11 2011 Great East Japan Earthquake and tsunami. Summary of the Fukushima Daiichi Disaster The earthquake on March 11 2011 off the east coast of Honshu Japans largest island reportedly caused an automatic shutdown of 11 of Japans 55 operating nuclear power plants. There were no coordinated arrangements at the national and local levels for responding to a nuclear emergency and a natural disaster occurring simultaneously. Fukushima Daiichi nuclear disaster a series of events beginning on 11 March 2011. The earthquake destroyed the external power supply of the nuclear reactor. On March 11 2011 a multiunit accident occurred at the Fukushima Daiichi plant on the northeastern Japanese coastline.
 Source: notes.nap.edu
Source: notes.nap.edu
A temporary exclusion zone of 20 km 12 mi was established around the plant. The earthquake destroyed the external power supply of the nuclear reactor. A temporary exclusion zone of 20 km 12 mi was established around the plant. On Wikipedia there is no listing for LORCA. On March 11 2011 a multiunit accident occurred at the Fukushima Daiichi plant on the northeastern Japanese coastline.

Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Accident On 11 March 2011 Japan was shaken by what became known as the Great East Japan Tohoku Earthquake. The movement was so severe that the country moved a few metres east the local coastline dropped and it triggered a tsunami which killed thousands of people. The legacy of the Fukushima nuclear disaster Five years ago on 11 March 2011 a large region of Japan was shaken for three minutes by a magnitude 90 earthquake. The tsunami resulting from the earthquake shut down the diesel generators and the main cooling system causing a series of nuclear meltdowns and hydrogen-air chemical reactions. It triggered a tsunami which swept over the main island of Honshu killing more than 18000 people and wiping entire towns.
 Source: newscientist.com
Source: newscientist.com
The Fukushima nuclear power plant accident was the result of collusion between the government the regulators and Tepco and the lack of governance by said parties said the report compiled by. The unfolding nuclear disaster at the Fukushima Daiichi reactor site in Japan is unlikely to be characterized by the accidental and unexpected sudden decline of the decay heat which is the key element of any loss of reactor coolant accident LORCA. On Wikipedia there is no listing for LORCA. A temporary exclusion zone of 20 km 12 mi was established around the plant. Context - What are the causes and consequences of the 11 March 2011 accident at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant in Japan.
 Source: in.pinterest.com
Source: in.pinterest.com
Although triggered by these cataclysmic events the subsequent accident at the. The Fukushima accident was an accident in 2011 at the Fukushima Daiichi Number One nuclear power plant in Japan. Fukushima Nuclear Disaster Congressional Research Service Summary The huge earthquake and tsunami that struck Japans Fukushima Daiichi nuclear power station on March 11 2011 knocked out backup power systems that were needed to cool the reactors at the plant causing three of them to undergo fuel melting hydrogen explosions and radioactive. The legacy of the Fukushima nuclear disaster Five years ago on 11 March 2011 a large region of Japan was shaken for three minutes by a magnitude 90 earthquake. Fukushima nuclear disaster summary.
 Source: tr.pinterest.com
Source: tr.pinterest.com
Summary of the Fukushima Daiichi Disaster The earthquake on March 11 2011 off the east coast of Honshu Japans largest island reportedly caused an automatic shutdown of 11 of Japans 55 operating nuclear power plants. The tsunami resulting from the earthquake shut down the diesel generators and the main cooling system causing a series of nuclear meltdowns and hydrogen-air chemical reactions. The Fukushima Daiichi nuclear power plant accident in March 2011 was the first occurrence showing that an extreme natural event that generated stress levels far beyond nuclear power plant design-basis values could lead to a core meltdown accident. Terrestrial radiological contamination resulting from the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear disaster and dismisses without supporting evidence its impact on non-human biota. Fukushima Daiichi nuclear disaster a series of events beginning on 11 March 2011.
 Source: cnet.com
Source: cnet.com
It was followed by a tsunami which resulted in waves reaching heights of more than 10 meters. At 246 pm a large magnitude 90 earthquake struck 180 km off the eastern coast resulting in an automatic shutdown of units 1 2 and 3 which were operating at the time. The accident at the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear plant was initiated by the March 11 2011 Great East Japan Earthquake and tsunami. Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Accident On 11 March 2011 Japan was shaken by what became known as the Great East Japan Tohoku Earthquake. The Fukushima Daiichi nuclear power plant accident in March 2011 was the first occurrence showing that an extreme natural event that generated stress levels far beyond nuclear power plant design-basis values could lead to a core meltdown accident.

It was followed by a tsunami which resulted in waves reaching heights of more than 10 meters. At 246 pm a large magnitude 90 earthquake struck 180 km off the eastern coast resulting in an automatic shutdown of units 1 2 and 3 which were operating at the time. The piping facility in the building the facilities for the external power supply and backup power were destroyed. The tsunami resulting from the earthquake shut down the diesel generators and the main cooling system causing a series of nuclear meltdowns and hydrogen-air chemical reactions. Although triggered by these cataclysmic events the subsequent accident at the.
 Source: en.wikipedia.org
Source: en.wikipedia.org
Major damage to the backup power and containment systems caused by the 2011 Tōhoku earthquake and tsunami resulted in overheating and leaking from some of the Fukushima I nuclear plants reactors. Later at the Fukushima Daiichi the tsunami which was one of the largest scale in history caused flooding of many of the power panels and the EDGs except for Unit 6 stopped resulting in the loss of all AC power and a loss of all the cooling functions. The tsunami resulting from the earthquake shut down the diesel generators and the main cooling system causing a series of nuclear meltdowns and hydrogen-air chemical reactions. The IAEA confirms extremely high levels of radioactive caesium were deposited northwest of the reactor site. The Fukushima Daiichi nuclear power plant accident in March 2011 was the first occurrence showing that an extreme natural event that generated stress levels far beyond nuclear power plant design-basis values could lead to a core meltdown accident.
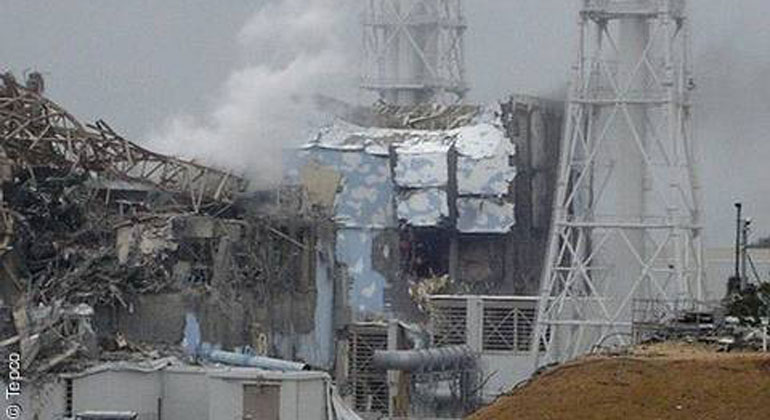 Source: sonnenseite.com
Source: sonnenseite.com
A temporary exclusion zone of 20 km 12 mi was established around the plant. Later at the Fukushima Daiichi the tsunami which was one of the largest scale in history caused flooding of many of the power panels and the EDGs except for Unit 6 stopped resulting in the loss of all AC power and a loss of all the cooling functions. Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Accident On 11 March 2011 Japan was shaken by what became known as the Great East Japan Tohoku Earthquake. The movement was so severe that the country moved a few metres east the local coastline dropped and it triggered a tsunami which killed thousands of people. Terrestrial radiological contamination resulting from the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear disaster and dismisses without supporting evidence its impact on non-human biota.
 Source: irsn.fr
Source: irsn.fr
Thus highly radioactive materials were released surrounding. The Fukushima accident was an accident in 2011 at the Fukushima Daiichi Number One nuclear power plant in Japan. Terrestrial radiological contamination resulting from the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear disaster and dismisses without supporting evidence its impact on non-human biota. Flooding of critical plant equipment resulted in the extended loss of onsite AC and DC power. Context - What are the causes and consequences of the 11 March 2011 accident at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant in Japan.
 Source: bfs.de
Source: bfs.de
The Fukushima Daiichi nuclear power plant accident in March 2011 was the first occurrence showing that an extreme natural event that generated stress levels far beyond nuclear power plant design-basis values could lead to a core meltdown accident. The earthquake knocked out offsite AC power to the plant and the tsunami inundated portions of the plant site. The Fukushima accident was an accident in 2011 at the Fukushima Daiichi Number One nuclear power plant in Japan. Context - What are the causes and consequences of the 11 March 2011 accident at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant in Japan. Fukushima nuclear disaster summary.
 Source: amazon.com
Source: amazon.com
A temporary exclusion zone of 20 km 12 mi was established around the plant. The Fukushima accident was an accident in 2011 at the Fukushima Daiichi Number One nuclear power plant in Japan. All three cores largely melted in. The next day 12th in the early morning the leakage of radioactive materials had been found in front of the main gate of the nuclear. Although triggered by these cataclysmic events the subsequent accident at the.
 Source: large.stanford.edu
Source: large.stanford.edu
Fukushima nuclear disaster summary. Fukushima Daiichi nuclear disaster a series of events beginning on 11 March 2011. Updated April 2021 Following a major earthquake a 15-metre tsunami disabled the power supply and cooling of three Fukushima Daiichi reactors causing a nuclear accident beginning on 11 March 2011. Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Accident On 11 March 2011 Japan was shaken by what became known as the Great East Japan Tohoku Earthquake. The Prime Minister declared a nuclear emergency on the evening of.
 Source: wikiwand.com
Source: wikiwand.com
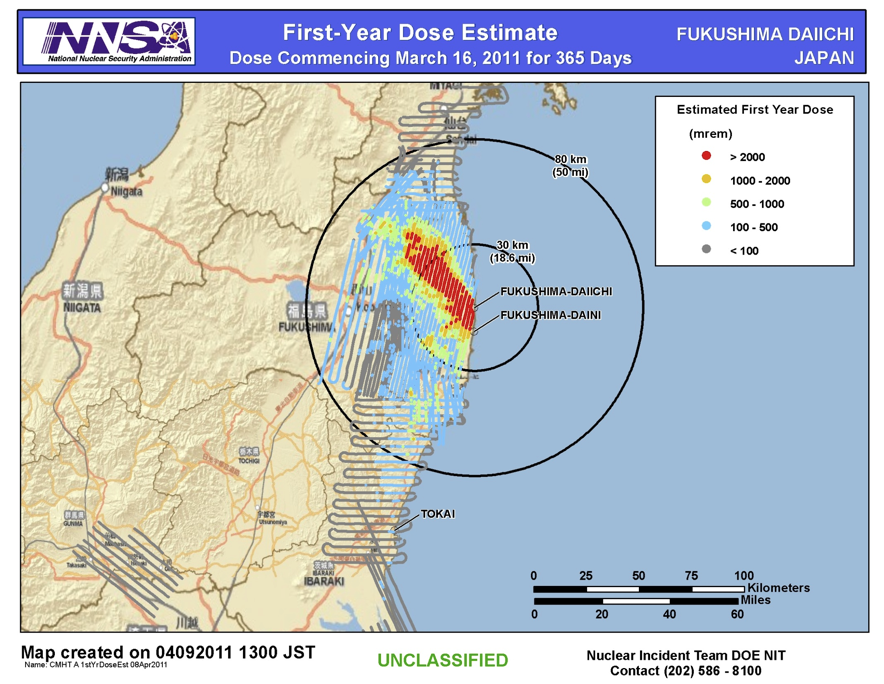
Respectively in this area it states that deposition densities between 1000 kBqm2 and 10 000. Terrestrial radiological contamination resulting from the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear disaster and dismisses without supporting evidence its impact on non-human biota. The IAEA confirms extremely high levels of radioactive caesium were deposited northwest of the reactor site. Respectively in this area it states that deposition densities between 1000 kBqm2 and 10 000. All three cores largely melted in.
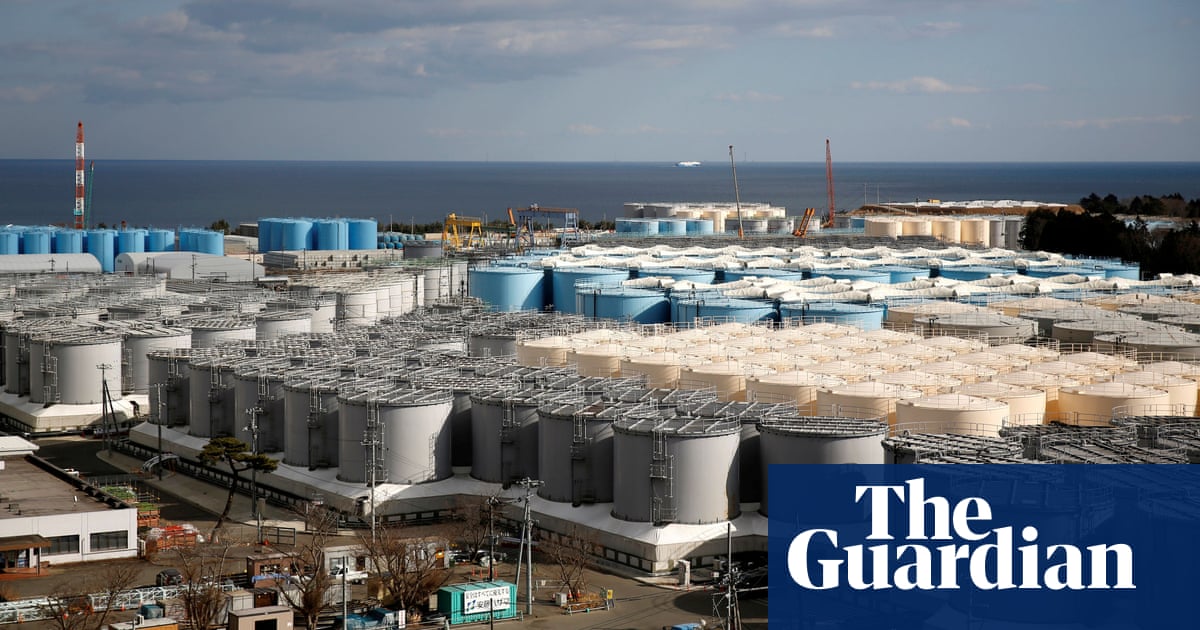 Source: theguardian.com
Source: theguardian.com
The unfolding nuclear disaster at the Fukushima Daiichi reactor site in Japan is unlikely to be characterized by the accidental and unexpected sudden decline of the decay heat which is the key element of any loss of reactor coolant accident LORCA. Major damage to the backup power and containment systems caused by the 2011 Tōhoku earthquake and tsunami resulted in overheating and leaking from some of the Fukushima I nuclear plants reactors. At 246 pm a large magnitude 90 earthquake struck 180 km off the eastern coast resulting in an automatic shutdown of units 1 2 and 3 which were operating at the time. This is a challenging accident for a nuclear power plant and is referred to as a loss of offsite power The reactor and its backup systems are designed to handle this type of accident by including backup power systems to keep the coolant pumps working. The next day 12th in the early morning the leakage of radioactive materials had been found in front of the main gate of the nuclear.
 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
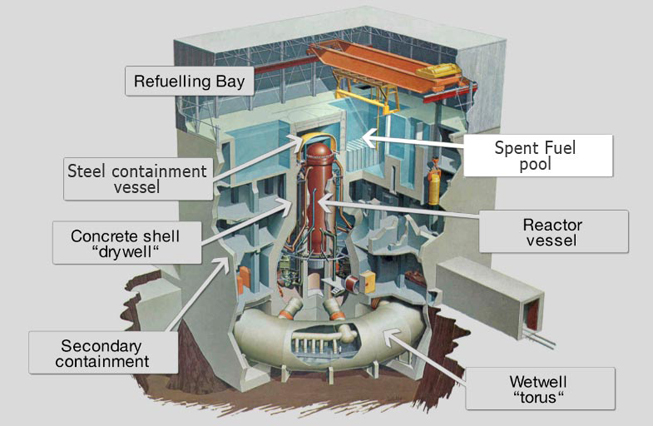
219 The fukushima daiichi accident. Later at the Fukushima Daiichi the tsunami which was one of the largest scale in history caused flooding of many of the power panels and the EDGs except for Unit 6 stopped resulting in the loss of all AC power and a loss of all the cooling functions. Major damage to the backup power and containment systems caused by the 2011 Tōhoku earthquake and tsunami resulted in overheating and leaking from some of the Fukushima I nuclear plants reactors. Fukushima Daiichi nuclear disaster a series of events beginning on 11 March 2011. Terrestrial radiological contamination resulting from the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear disaster and dismisses without supporting evidence its impact on non-human biota.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
All three cores largely melted in. Updated April 2021 Following a major earthquake a 15-metre tsunami disabled the power supply and cooling of three Fukushima Daiichi reactors causing a nuclear accident beginning on 11 March 2011. There were no coordinated arrangements at the national and local levels for responding to a nuclear emergency and a natural disaster occurring simultaneously. Later at the Fukushima Daiichi the tsunami which was one of the largest scale in history caused flooding of many of the power panels and the EDGs except for Unit 6 stopped resulting in the loss of all AC power and a loss of all the cooling functions. On March 11 2011 a multiunit accident occurred at the Fukushima Daiichi plant on the northeastern Japanese coastline.
 Source: iaea.org
Source: iaea.org
Later at the Fukushima Daiichi the tsunami which was one of the largest scale in history caused flooding of many of the power panels and the EDGs except for Unit 6 stopped resulting in the loss of all AC power and a loss of all the cooling functions. The Fukushima Daiichi nuclear power station located in the Pacific Ocean coast received huge damage by the earthquake and tsunami. It is the second worst nuclear accident in the history of nuclear power generation behind the Chernobyl disaster. The accident at the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear plant was initiated by the March 11 2011 Great East Japan Earthquake and tsunami. Respectively in this area it states that deposition densities between 1000 kBqm2 and 10 000.
This site is an open community for users to do sharing their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site beneficial, please support us by sharing this posts to your preference social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also save this blog page with the title fukushima daiichi nuclear disaster summary by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.






